Busting benzene, lab-grown embryos — the week in infographics
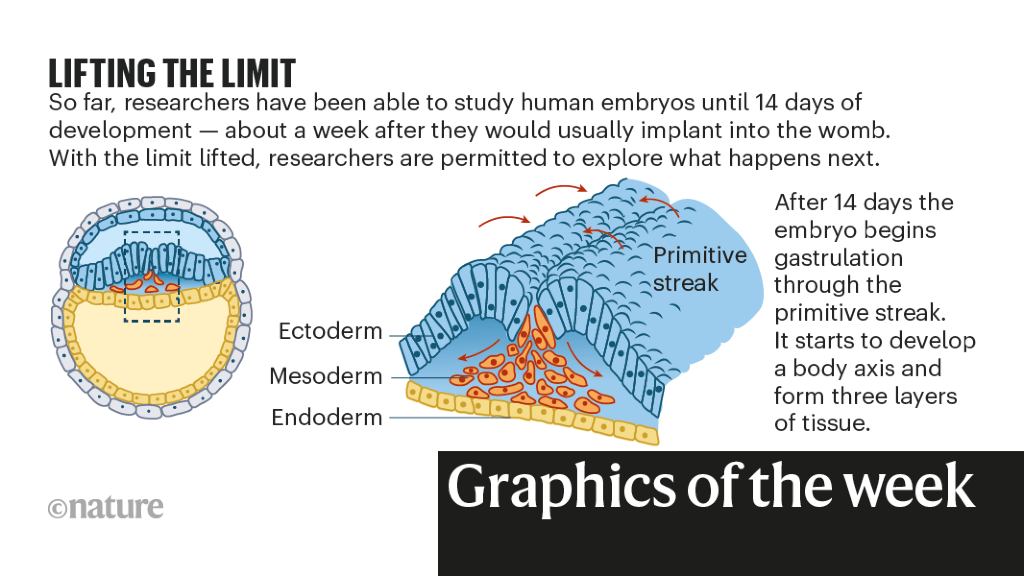
The way forward for lab-grown embryos
In May, the International Society for Stem Cell Research launched new tips that relaxed the 14-day rule, a global consensus that human embryos must be cultured and grown in the lab solely till 14 days post-fertilization. The change permits scientists, in international locations the place it’s authorized, to hunt permission to proceed analysis past this level.
Such research may reveal what happens during human development after the embryo would normally have implanted in the uterus. Roughly between days 14 and 22, it enters gastrulation, when the physique’s foremost sample emerges and the foundations are laid for organ technology. Studying these phases would enable scientists to higher perceive the almost one-third of being pregnant losses and quite a few congenital disabilities regarded as triggered at these factors in improvement.
How people journeyed into Arabia
Humans and our hominin family have repeatedly dispersed from Africa into the Arabian Peninsula over the previous 400,000 years. We know that people might need reached Australia as early as 65,000 years in the past (65 ka). However, when and the way typically they dispersed from Arabia throughout southern Asia to India and southeast Asia has been unclear. A Nature paper published this week studies the excavation of artefacts at the Khall Amayshan web site (referred to as KAM 4) in Saudi Arabia, which correspond to 5 intervals of occupation. Together with different dated proof from the Levant, Asia and Australia (just a few examples of that are proven right here), a more complete picture is emerging of these early dispersals. It suggests there have been pulses of immigration linked to intervals of rainfall — creating ‘green’ home windows when situations have been beneficial.
Breaking the unbreakable benzene
Aromatic molecules equivalent to benzene are a few of the most helpful constructing blocks of chemistry. But benzene rings, which include six carbon atoms linked in a hexagon, are additionally exceptionally secure, and only a few reactions are recognized to interrupt them open.
A course of referred to as hydroisomerization breaks up benzene rings at excessive temperatures, however is unselective, producing a mix of hydrocarbon merchandise, proven in (a). Dioxygenase enzymes also can do the job, however end result in a single product referred to as muconic acid (b). Researchers have now reported another method: a copper-catalysed response in which benzene derivatives react with oxygen and an oxidant (sodium azide; NaN3) to provide alkenyl nitriles (c). The response is believed to proceed by way of an unstable intermediate referred to as a bis(nitrene). The authors present that their benzene-busting protocol can work on molecules with difficult buildings, offering a brand new method for chemically manipulating pure merchandise, dyes and prescribed drugs.
The bond that breaks is highlighted in pink, and the carbon atoms in the benzene ring are numbered to indicate how they translate from the beginning materials to the product. R represents a variety of reactive chemical teams; L is a ligand molecule; Cu, copper.



